- Introduction
- Coupling constants
- Chemical shifts
- Carbohydrates
- Nucleosides
Nucleotides
νi=P*cos(νmax+(i-2)*4*π/5)
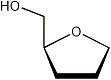
Using the torsions ν0-ν4 the torsions between the ring protons can be derived. Together with an appropriate Karplus equation[2] the corresponding coupling constants can be estimated, or experimental coupling constants can be used to determine the phase (P) and puckering (νmax) of the ring.
Literature
[1] C. Altona and M. Sundaralingam; J. Am. Chem. Soc. 94 (1972) 8205-8212.[2] C.A.G. Haasnoot, F.A.A.M. DeLeeuw and C. Altona; Tetrahedron 36 (1980) 2783-2792.
Instructions
- Choose the correct substituents for positions C1'-C3' (or equivalent, e.g. C2,C3,C4 in fructofuranose).
- Choose the correct stereochemistry either by specifying the orientation of each substituent (check if below the plane of the ring) or select from ribo, arabino, &c below.
- Enter coupling constants if known.